Reliable and uninterrupted operation of the car depends on the three types of liquids poured into the car. These include fuel, coolant and oil. The quality and level of their fullness affects the performance of other systems and mechanisms. It is also necessary that the interpenetration of these liquids does not occur in the systems not intended for them. Such mixing may lead to undesirable consequences.
For example, one of the reasons why engine oil foams may be antifreeze in the crankcase with oil. Therefore, we will deal with all the causes and effects of foaming, as well as find out how to avoid this phenomenon or minimize it.
Content
- 1 Engine lubrication system
- 2 Causes of oil foaming
- 3 Depressurization of the lubrication system
- 4 Symptoms of mixing and self-diagnosis
- 5 Chemical incompatibility of oils
- 6 Condensate
- 7 Need to get rid of foaming
Engine lubrication system operation
Увеличением производительности силовой установки за счет снижения сил трения при работе занимается system смазки. Дополнительной ее функцией является отвод лишнего тепла от узлов и отдельных деталей. Чтобы максимально эффективно выполнять свои функции масло должно соответствовать рабочим характеристикам и эксплуатироваться в установленном производителями режиме.
The lubrication system of the internal combustion engine consists of the following components:
- pallet oil sump;
- pumppumping fluid through the system;
- system filtering from pollution;
- wiring the contour of the channels, tubes and hoses to lubricated nodes.
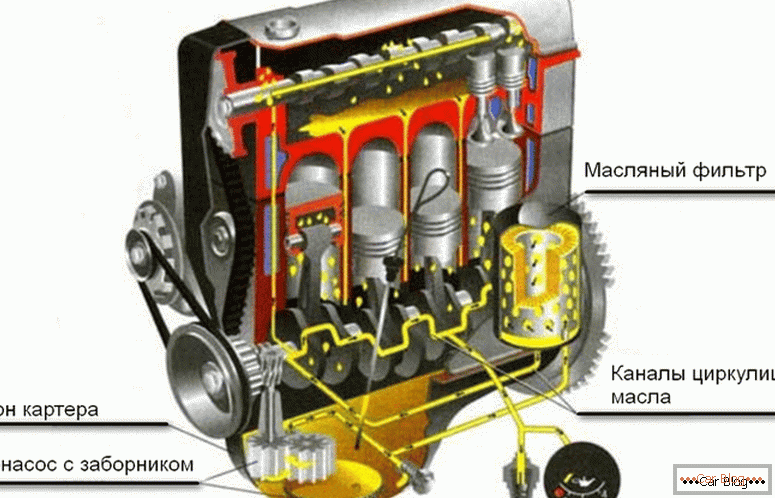
Engine lubrication system
The system is hermetically sealed from the ingress of foreign liquids. It is provided with gaskets, seals and seals. There are established norms for the replacement of oil.
С момента запуска работы мотора шестеренчатый pump начинает нагнетать давление в системе и подает масло через фильтр на узлы, работающие с повышенным износом: шейки коленвала и рапредвала, клапанный механизм. Сливаясь обратно в pallet и попадая на шатунный механизм, масло разбрызгивается на стенки цилиндров. Оттуда оно убирается маслосъемными кольцами поршневой системы. Процесс происходит беспрерывно в течение работы двигателя.
Causes of oil foaming
Кроме смазочной системы блок цилиндров оборудован охлаждающей системой. Она распределена по каналам в блоке. Рабочей жидкостью в основном в ней является тосол, забирающий тепло от мотора и способствующий охлаждению рабочих органов. Эта system также герметизирована. Циркуляцию в ней обеспечивает лопастной pump (помпа).
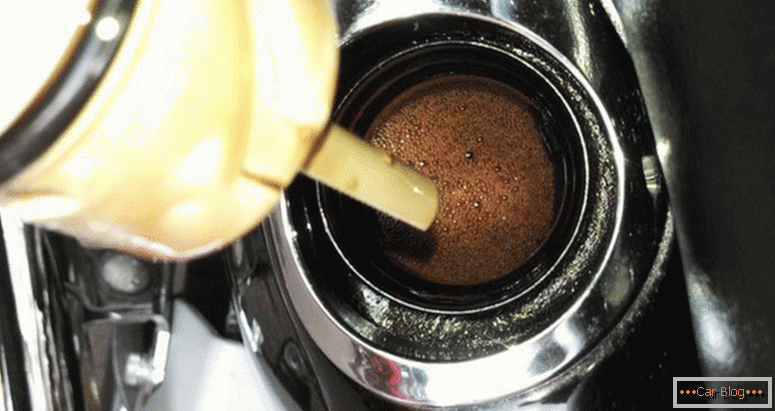

Oil foams in ICE
If the gasket is worn or broken between the cylinder head and the block itself, it will ensure that antifreeze penetrates the lubrication system. Because of this, oil may foam.
The second most common cause of foam may be the incompatibility of oils. When replacing it from the lubrication system, it is impossible to remove absolutely all liquid. The remaining small amount of the “old” liquid may not be combined in chemical parameters with the “new” one. This interaction leads to the formation of air bubbles.
See also: How to check the serviceability of the catalystDepressurization of the lubrication system
Due to the communicating unauthorized channels coolant penetrates under the cylinder head. The installed gasket should perform one of its functions with high quality, which consists in blocking such an interaction. A metal protective edge is mounted on its ends, clamped when the gasket is installed, and protects it from the effects of high temperatures and compression pressure.
In the event of cracks or ruptures of such a protective element of the gasket, depressurization occurs. Охлаждающая жидкость получает возможность проникать в цилиндры двигателя, а затем по каналам спускается в pallet. Смешиваясь там с маслом, она образует нежелательное вспенивание. Его можно заметить при открытии крышки с заливного отверстия на блоке цилиндров.
In addition to the gasket, the perpetrators of depressurization may be cracks in the body parts: the block or the cylinder head. Overheating of the motor, various impacts, and physical aging of the metal contribute to their occurrence. Through such cracks, penetration of foreign fluids into the lubrication system can also occur.

Crack in the housing
Such problems can be solved by replacing the gasket or body part (cylinder head). In rare cases, soldering or welding of such cracks is allowed. This procedure is unlikely to solve the problem of sealing for a long time, since it requires special training and experience in welding with aluminum or cast iron.
Symptoms of mixing and self-diagnosis
There are main signs of depressurization of the system:
- the presence of oil stains on the liquid cooling system;
- reduced compression in engine cylinders;
- oil drips from under the head of the block;
- regular reduction of antifreeze in the expansion tank;
- the constant presence of white smoke in the exhaust gases.
Carrying out simple diagnostic measures will eliminate the additional costs associated with a trip to the station. In addition to visual inspection of the antifreeze level and the presence of leaks, you can remove the cylinder head and inspect it for cracks or chips.
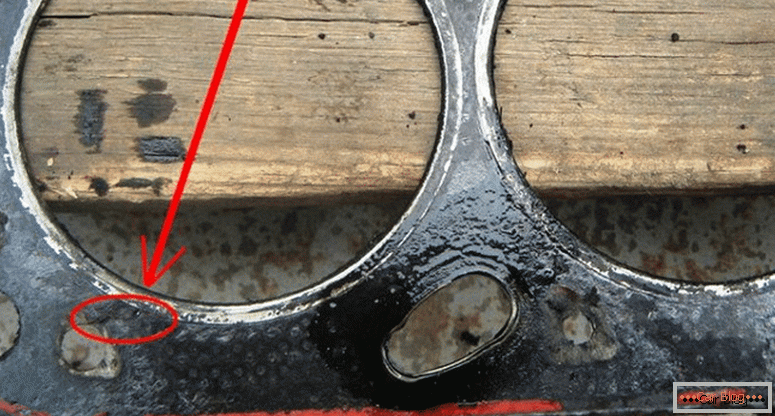

Unsealed gasket
A test will also help with checking the exhaust for oil. To do this, the ignition is turned on and the engine warms up to operating temperature. The exhaust pipe closes for a few seconds with a clean sheet of paper. If the leaf becomes a little wet, and oily drops remain on it after drying, this indicates leaks. Work is needed to eliminate them.
If there are no such signs, then most likely, the problem is created for other reasons.
Chemical incompatibility of oils
Topping up the oil должен проводиться такого же вида, которое было залито первоначально. Минеральное с синтетическим смешивать не стоит. Влитая «минералка» в «синтетику» нарушит однородную структуру жидкости. Это связано с тем, что полученное после нефтяной перегонки минеральное масло имеет больший разброс по размерам углеводородных молекул в структуре, чем изготовленное из газов, более однородное синтетическое.

Topping up the oil
The inconsistency in the size of the molecules of "mineral water" affects the behavior during sudden changes in operating temperatures. It also affects viscosity, lubricating properties and freezing point.
In addition to the base material, additional additives are present in the lubricating fluid. In different oils, they differ in the nature of the interaction with the surrounding system and among themselves. Sometimes additives can react with other chemicals from topped-up oil, and lead to undesirable effects, such as foaming.
See also: Check hydraulic liftersCondensate
Water entering the lubrication system changes the properties of the oil. Complete dissolution of oil in water will not occur. However, with prolonged stirring, a suspension may form in the form of an emulsion. She sees the driver on the dipstick, checking the oil level. Such a "cocktail" is formed regardless of the quality of the oil.
Water condensate forms in the system from air. It accumulates on the cold elements of the engine, if there is a significant difference in ambient temperatures and metal parts. Most often, its formation occurs in the off-season and in the winter in a poorly heated garage. Drops of condensate drain into the oil and accumulate, mixing with it. The result is a foam.

Engine oil change
To combat this phenomenon, it is necessary to warm up the motor well during cold weather so that the water can evaporate from the surface or condensate does not appear. You can also insulate the engine for quick warming up.
Need to get rid of foaming
It is necessary to get rid of foamed oil. It does not perform its functions for high-quality and uniform lubrication. The structure of such a substance is heterogeneous. Air bubbles enveloped in a dense shell, have a different density with oil. This is not conducive to the rapid removal of heat from the nodes. Unwanted motor overheating occurs.
Such bubbles pass badly through the channels of the “shirt” of the cylinder block. It turns out a weak circulation of oil in the system, changing the viscosity of the substance.
When an emulsion is formed with condensate, the oil does not perform its lubrication work. In addition to overheating due to an increase in the friction coefficient, this all leads to the formation of scuffing, wear to the rubbing surfaces, and failure of the mating elements. Strained condensate can freeze in the flow channels, blocking the circulation of oil. This leads to hydraulic shocks and more severe consequences with the engine.
Therefore, it is necessary to regularly monitor the condition of the oil, and in the event of such a condition, to carry out the necessary work to eliminate the identified problems.



