Automakers strive to ensure a decent life of their products as a whole, as well as their individual elements. However, there are ways to help expand the framework set by these companies. An example is the resuscitation of the main electrical device in the car. In the article we will show you how to restore a car battery so that it will work for several additional months or not.
Buying a new battery in this case is not canceled, but only postponed for this period. Initially high-quality batteries are suitable for experiments. Related materials to help “revive” the developed unit are available to any car owner.
Content
- 1 Common causes of failure of the battery
- 2 External battery damage
- 3 Internal battery breakdowns
- 4 Ways to restore the battery
- 5 How to properly operate the battery
Common causes of failure of the battery
When the battery undergoes frequent complete discharge and prolonged downtime in such a position, the main battery “disease”, sulphation of the plates, occurs during this operation. The consequence of this process is a noticeable drop in capacity. Because of this, such a battery can not crank the starter during the start of the motor.
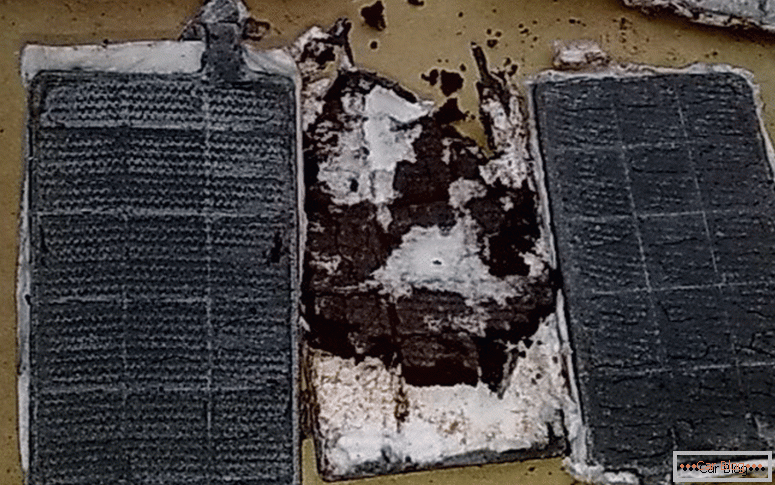
Sulfation of battery plates
Learn about the beginning of sulfation can be on several grounds:
- increased voltage at the terminals;
- noticeable heating plates during operation;
- sometimes electrolyte boils;
- reduced charge capacity.
Another cause of failure can be the destruction of the plates, which leads to a short circuit between them. Sometimes there is a complete separation of the plate from its place. The reason for this damage can be a surplus of voltage applied to charge the battery with a lack of electrolyte in the tank.
You need to know that both insufficient and excessive charge can lead to the destruction of the car battery.
After carrying out repair work with the battery, in order to revive the car battery, it will be necessary to get rid of the source of destruction of the electrical element.
External battery damage
Before starting to fix, we define the types of problems and the possibility of their elimination. As external faults, terminal oxidation is present. Due to the coating layer of scale, there is no quality contact between the surface of the battery electrode and the wire in contact with it.
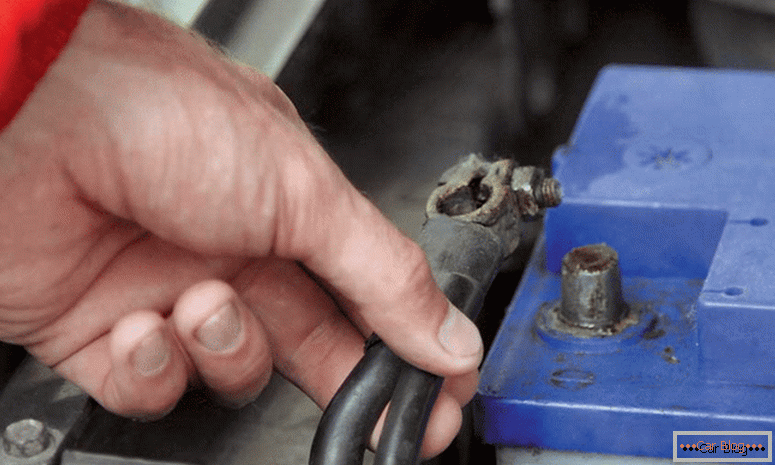

Cleaning the surface can restore the electrical characteristics of the battery. Sometimes the terminal is mounted tightly enough, it clings to the electrode, so you need to unwind the connection and check the presence of a good mate.
The second most common external problem is damage to the battery case. This happens due to external mechanical damage or due to internal faults. Repairing a car battery and plugging a hole is only possible on serviced batteries. To do this, the contacts are folded back, the battery is removed, the remaining electrolyte is fused and the outer wall is soldered with a plastic patch. You can check the tightness with distillate. Only then fresh electrolyte is poured into the tank.
See also: How does the adaptive cruise control in the carInternal battery breakdowns
The main problem that spoils the battery from the inside, is the coating of the plates with salts of the reaction of acid and lead. They prevent the movement of charged particles from one electrode to another. In parallel, the resistance increases, which leads to a decrease in the total battery capacity. The early periods of such a process are reversible, but if the reaction significantly damaged the plates, then the recovery of the unit is impossible.
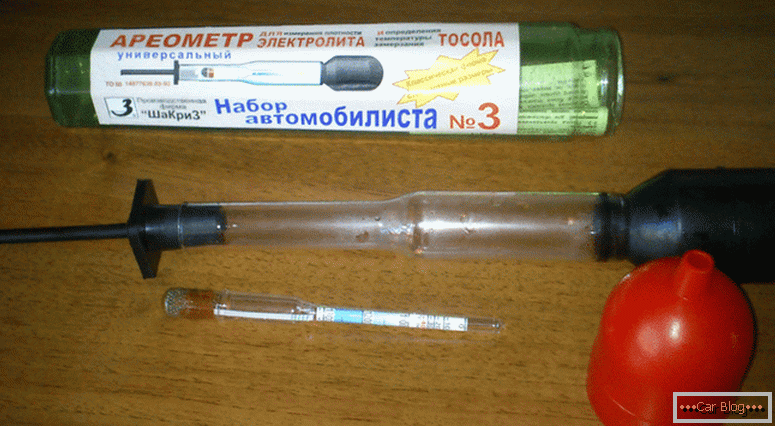
Electrolyte density measuring device
Sometimes it is possible for particles to fall from the plates, leading to a short circuit. If this happened not so long ago, then washing out the inside with distilled water will help. In order not to get the hull blow-up from severe long frosts, you should not leave the battery in the car. Expanded due to this process, the electrolyte will destroy the design of the battery, which after such a "stress" will not be able to recover.
Ways to restore the battery
We describe the most popular ways to resume performance, in which the repair of a car battery will give it an extra lifetime.
- To conduct a stress control training cycle, a charger with a voltmeter, a device for measuring the density (hydrometer), and any consumer of electricity (for example, an incandescent lamp) are used. The process begins with a full charge of the problem battery. For this purpose, a current of approximately 10% of the stated battery capacity is used. In batteries with 55 Ah you need to apply a current of 5.5 A. Then the density in each tank (can) is controlled. The parameter must be about 1.27 g / ml. When a low density is detected, it is necessary to set the required parameter, and then recharge the battery for another half an hour. Then we discharge the system with the help of a lamp, which should “eat up” no more than 10% of the battery capacity. Consumer power is at the multiplication of the current and voltage source. The maximum discharge can be considered indications on a voltmeter at the level of 10.2 V. It is required to measure the time during which the process takes place. For new batteries this procedure takes about 10 hours. Less time means lower capacity. After discharging it is required to throw charging wires back onto the terminals. Several such cycles save the battery from a little sulphation and return the lost capacity.
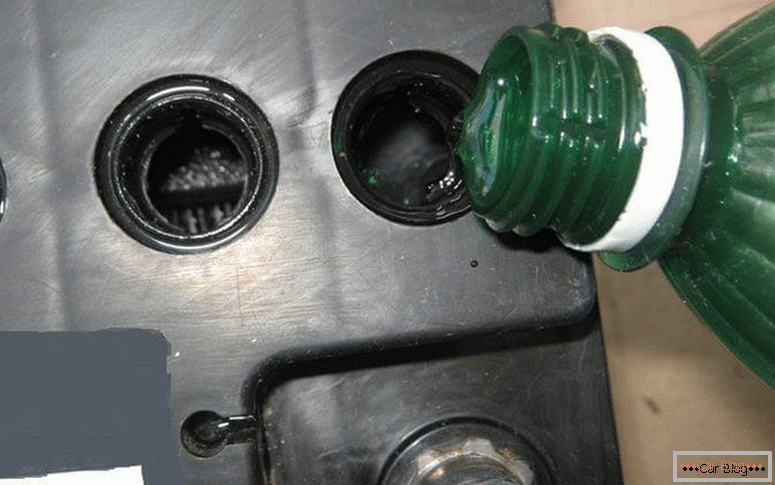

Washing the insides of the battery
- The second method requires a special generator to form reversible currents. The method provides for the charge of small currents. When the plates in a battery are damaged in a small area with sulfate, then you can use a current from half a meter to two units for charging. The period of such charging can be up to two days. This procedure can be completed after the measuring voltage of the terminals is stable and the electrolyte density does not change much more than two hours.
- The third method is longer and can be carried out within a few days. It requires to drain the entire electrolyte from the battery, and in the banks to collect the distillate. Next, put the battery in charge and wait for the boiling to start, but do not bring it to that. As soon as the temperature rises significantly, it is necessary to reduce the supply voltage and in this mode hold for several hours so that the sulfate salt dissolves in water. Then pour the mixture and refill it with clean distillate. Also bring to a boil, but without a violent reaction and repeat until the density of the poured liquid is stable and low. This indicates the cleansing of the plates.
- Some craftsmen use an aggressive version of chemical cleaning. It will need a mixture of Trilon B and ammonia. The electrolyte is removed from the battery, and the cavities are washed with distillate. After that, we pour in a washing water solution of 5% ammonia and 2% Trilon B. It is necessary to do the operation with protective glasses and rubber chemical gloves, since during the topping up a vigorous chemical reaction will take place. After the termination of its active phase, all the liquid can be drained and washed containers. Next, pour the electrolyte and charge the battery.
Battery protection
How to properly operate the battery
You can delay the repair of a car battery and extend its service life by following simple rules:
- at least once a season it is necessary to control the density of the electrolyte;
- during frosts above 20-25With the need to bring the density to 1.35-1.4 g / ml;
- to charge the battery, a current of less than 10 times the numerical value of the capacitance is used;
if the car can be on open parking during frost from -25Since, it is desirable to shelter or take it with you so that the frozen electrolyte does not disable the unit.



