Rotary engines, also called Wankel engines, are motors where the main working element is planetary circular motion. This engine is significantly different from its piston counterparts engine.
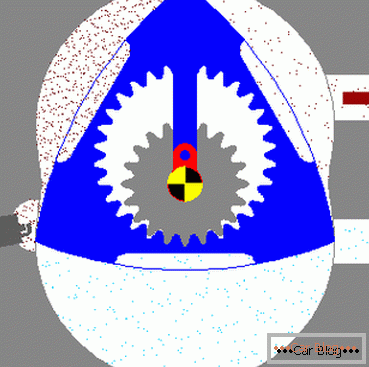
In the design of such an engine, a piston with three faces (rotor) is used, which forms circular motions in the cylinder of a special profile. In practice, you can meet and rotor of other forms.
Principle of operation and components
The rotor, which has three faces, moves along the epitrochoidal plane of the cylinder, as a result of which the volumes of the combustion chambers of the cylinder are cut off using three valves. The sealing plates of the end and radial type, under the action of gases, are pressed to the cylinder due to the centrifugal force and the band spring. On the eccentric axis, the circular motion of the rotor is transmitted. The eccentric axis itself, rotates on bearings, and transmits torque, directly to the transmission mechanisms.
Engine mounted on cars VAZ, had the following characteristics:
- 103 kW / 6000 rpm - nominal power;
- 103 kg engine weight;
- 1,308 cm3 - the working volume of the motor;
- 125,000 km - resource to the first overhaul.
Features of the RPD

The principle of operation of the rotary engine
Benefits
Along with the usual ICE, rotary had a low level of vibration. This ability RAP acquired by reciprocating - translational motion, which was converted into a rotational motion. Good ability dynamics of such engines. A car with rotary engines could accelerate to 100 km / h at high revs, while not tolerating heavy loads. Power RPD was achieved by the absence of a crankshaft and connecting rods, while creating a small mass of moving parts in a rotary engine. The lubrication system in such engines was practically absent. Oil is added directly to the fuel. And already the fuel is an air mixture, itself lubricates friction pairs. The rotary engine has a small size, so the engine compartment allows you to maximize your usable space. For example, a conventional four-stroke engine is almost twice the size of a rotary engine.
See also: 4th generation HBO - probable causes and symptoms of malfunctiondisadvantages
The quality of the spark plugs of such engines should be as good as possible. Since the combustion chamber, which still has a small volume, an extended shape and a high temperature of combustion, while with poor quality candles, it can be difficult to ignite the fuel mixture. Increased oil consumption. Due to constant exposure to friction of work surfaces. From practice we can say that rotary motors can consume from 400 grams to 1 kg of oil per 1000 km.
Applicability of rotary engines
NSU Spider became the first mass cars to receive a rotary “heart”. But along with the constant breakdowns and shortcomings of such motors, the owners often applied for a warranty to NSU Motorenwerke, which produced them. So the company began to suffer an economic collapse, and soon suffered bankruptcy. Between 1964 and 1967, only 2,375 cars with a rotary engine from NSU Motorenwerke were produced. In 1967, the NSU Spider was discontinued and replaced with the NSU Ro80 with a second-generation rotary engine. Ro80, in ten years, has produced more than 37,000 cars with RAP.

More successful manufacturer of RPD became engineers of Mazda. I must say Mazda and now remains the only mass producer of cars with rotary engines. Serial RPD stood on the Mazda RX - 7 since 1978. And since 2003, the Mazda RX - 8 has received such engines. The RX - 8 is still the only production car with a rotary engine.
See also: Diesel engine