Any car with an internal combustion engine has a gearbox in its design. There are many varieties of this unit, but the most common type is a manual transmission (manual transmission). She is equipped with both domestic and foreign cars.
Content
- 1 Purpose Manual
- 2 Principle of operation and device
- 2.1 Coupling
- 2.2 Gears and shafts
- 2.3 Synchronizers
- 3 shift process
- 4 Advantages and disadvantages of manual transmissions
Purpose Manual
The gearbox is used to change the gear ratio of the rotational speed from the engine to the wheels. The method of switching between the steps (gears) of this gearbox is manual (mechanical), which gave the name to the whole node. The driver independently decides which of the fixed values of the gear ratio (gears that engage) should be included in the current moment.
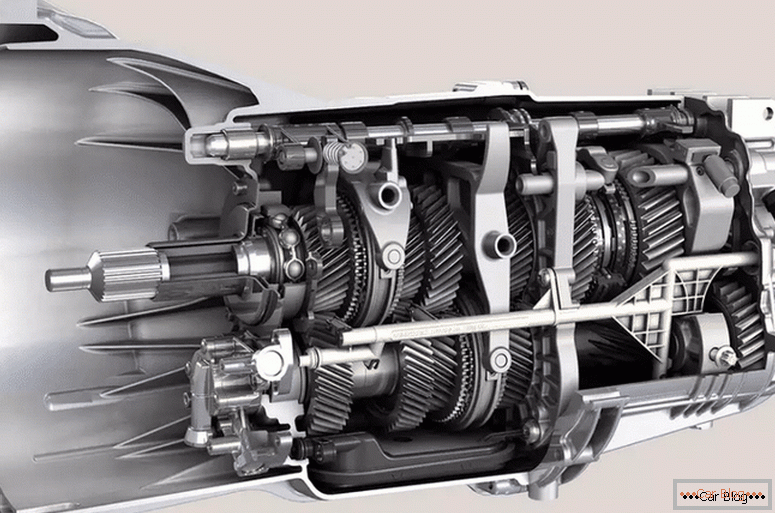
Modern Manual
In addition, manual transmission allows you to switch to reverse mode, in which the car moves in the opposite direction. There is also a neutral mode when there is no transfer of rotation from the motor to the wheels.
Principle of operation and device
The gearbox is a multistage closed gear. Helical gears have the ability to alternately be engaged and change the speed between the input shaft and the output. This is the principle of operation of the gearbox.
Clutch
Mechanical transmission is paired with a clutch. This node allows you to temporarily disconnect the engine from the transmission. Such an operation makes it possible to switch gears (steps) without serious consequences without turning off the engine speed.

The clutch block is necessary, since a considerable torque passes through the manual transmission.
Gears and shafts
In any gearbox of traditional design, the axles of the shafts are located parallel to the gears on which they are based. The common body is called the crankcase. The most popular are the three-shaft and two-shaft companies.
In the three-shaft there are three shaft:
- the first is the presenter;
- the second is intermediate;
- the third is the slave.
The first shaft is connected to the clutch, splines are cut on its surface, along which the driven clutch plate moves. From this axis, rotation is transmitted to an intermediate axis rigidly connected to the gear shaft of the input shaft.
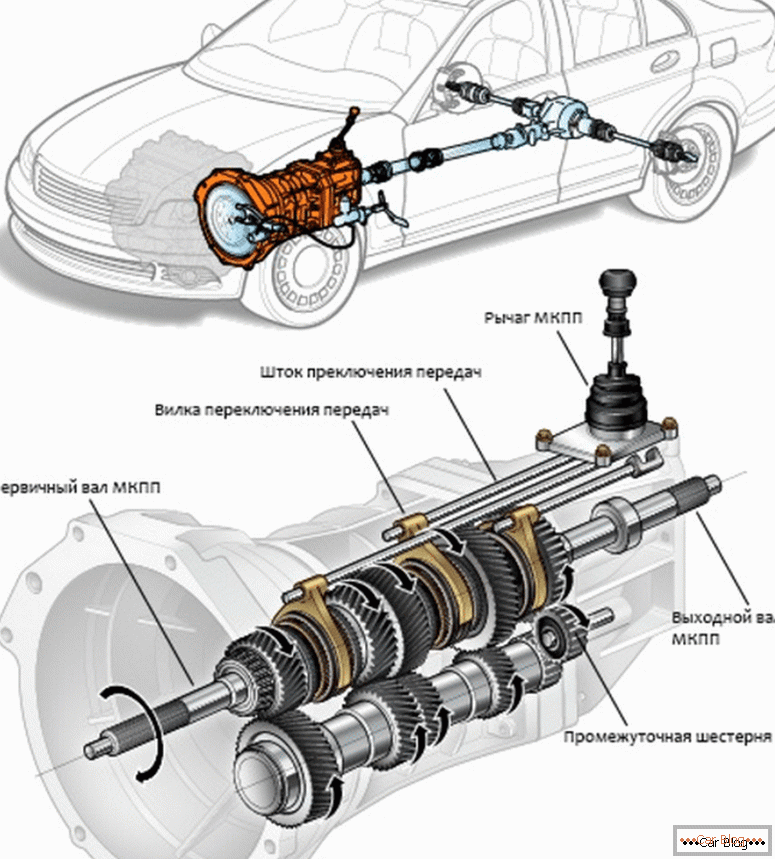
The manual transmission shaft has a specific location. It is coaxial with the master and connected to it through a bearing inside the first shaft. This ensures their independent rotation. The gear units from the driven axle do not have a rigid fixation with it, and the gears are delimited by special synchronizer couplings. The latter just rigidly sit on the driven shaft, but are able to move along the axis along the slots.
The ends of the couplings are equipped with toothed rims that can connect with the same rims located on the ends of the gears of the driven shaft. A modern gearbox device implies the presence of such synchronizers in all forward gears.
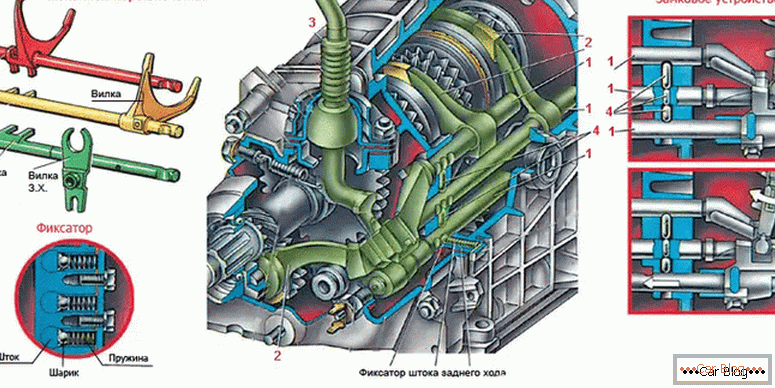
During the activation of the neutral mode, the free rotation of the gears occurs, and all the synchronizer couplings are in the open position. When the driver squeezes the clutch and switches the lever to one of the steps, then at this time the fork in the gearbox moves the clutch into engagement with his pair on the gear end. So the gear is rigidly fixed with the shaft and does not scroll on it, but provides the transmission of rotation and effort.
See also: How does the differential carFrom the driven shaft, the transmission of torque and revolutions to the drive wheels is carried out through the driveshaft (on the rear-wheel drive) or through the gearbox and CV Joints (on the front-wheel drive). When the synchronizer engages directly the drive and driven shafts without the participation of gears, then the box ensures maximum efficiency. For back speed, an intermediate “parasitic” gear is installed, changing the rotation to the opposite.
Most manual transmissions use gears with an oblique tooth, capable of withstanding greater efforts than spur teeth, and they are also less noisy. They are made of high-alloy steel, after which they are quenched by high-frequency current and normalized to relieve stresses. At the expense of it the maximum service life is provided.
For the two-shaft box, the connection of the drive shaft with the clutch unit is also provided. In contrast to the three-axis design, a block of gears is located on the leading axis, and not one. There is no intermediate shaft, and parallel to the leader is the driven shaft. The gears on both axles rotate freely and are constantly engaged.
The driven shaft is equipped with a rigidly fixed drive gear of the main transmission. Between the other gears are synchronization clutches. Such a scheme of a mechanical gearbox in terms of synchronizer operation is similar to the three-shaft scheme. The difference lies in the absence of direct transmission, and in that each step has only one pair of connected gears, and not two pairs.
Two-shaft manual gearbox device has a higher efficiency than the three-shaft, however, has a limitation on increasing the gear ratio. Due to this feature, the design is applied only in passenger cars.
Synchronizers
All modern mechanical gear boxes are equipped with synchronizers. Without them, the machines had to double-squeeze, so that the peripheral speeds of the gears became equal, and it was possible to switch the steps. Also, synchronizers are not put on the gearbox with a large number of gears, sometimes up to 18 steps, characteristic of special equipment, since it is technically impossible. For speed shifting, sports cars may not have synchronizers in manual transmissions.
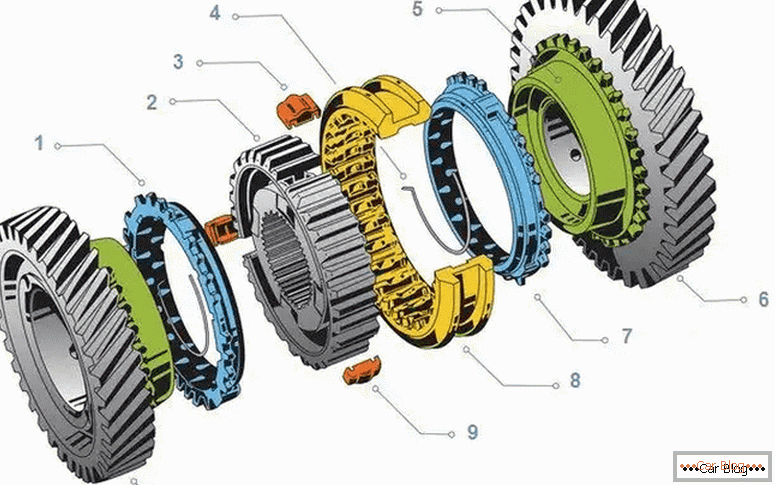
Synchronizer ICP
Легковые автомобили, используемые большинством водителей, оснащены синхронизаторами, так how does a car's gearbox work без них менее дружелюбно. Эти элементы обеспечивают бесшумность эксплуатации и выравнивание скоростей шестеренок.
The inner diameter of the hub has splined grooves, due to which the movement along the secondary shaft is carried out. At the same time, such rigidity ensures the transfer of large forces.
The synchronizer works in this way. When the driver starts the transmission, the clutch is fed to the side of the desired gear. During the transfer, the force moves to one of the clutch locking rings. Due to the different speeds between the gear and the coupling, the tapered surfaces of the teeth interact with the help of friction force. She turns the locking ring on the support.
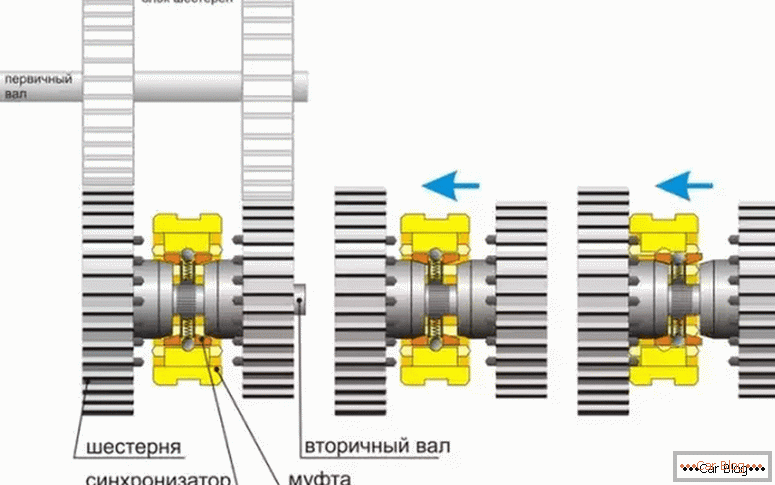
Synchronizer operation
The teeth of the latter are installed against the teeth of the coupling, so the subsequent displacement of the coupling becomes impossible. The clutch comes without reaction in engagement with a small crown on the gear. Gear due to such a connection is rigidly blocked with the clutch. This process takes place in a fraction of a second. One synchronizer usually provides the inclusion of two gears.
Gear shift process
The corresponding mechanism is responsible for the switching procedure. For cars with rear-wheel drive, the lever is mounted directly on the body manual. The whole mechanism is hidden inside the unit housing, and the shift knob directly controls it. This arrangement has its advantages and disadvantages.
See also: Signs of malfunction clutch release bearingPros:
- simple in construction plan;
- providing clear switching;
- more durable design for operation.
Minuses:
- there is no possibility to use the design with the rear motor;
- not used on front wheel drive cars.
Machines with front axle equipped with a gear lever in such places:
- outdoor between the driver and the front passenger seat;
- on the steering column;
- near the instrument panel.
The remote control box for front-wheel drive cars is carried out with the help of bolts or wings. This design also has its own characteristics.
Pros:
- comfortable more independent arrangement of the lever for gear shifting;
- vibration from the box is not transmitted to the manual transmission lever;
- Provides greater freedom for design and engineering layout.
Minuses:
- less durability;
- backlash may appear over time;
- Periodic, qualified adjustment of the dead weight is required;
- clarity less accurate, unlike the location directly on the body.
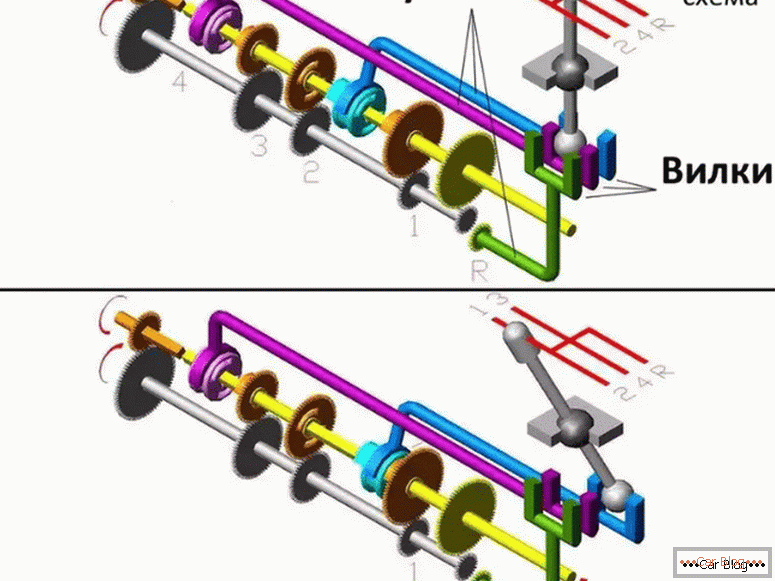
Although there are different drives for the mechanism of on / off gear, but the mechanism itself in most gearbox has a similar design. It is based on movable rods that are in the housing cover, as well as forks rigidly fixed on the rods.
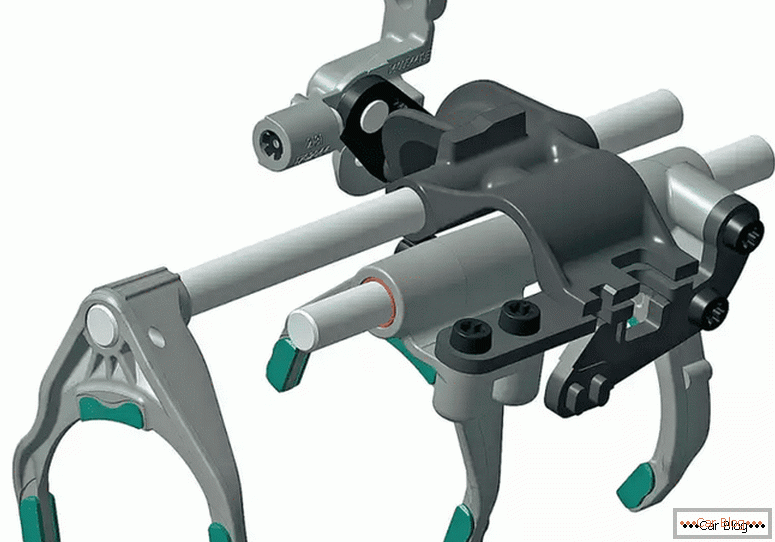
Gear Shift Lada Grant
The semicircular forks enter the groove of the synchronizer coupling. Additionally, gearboxes are located in the manual transmission, which will save the mechanism from failure to turn on or from unauthorized disengagement of gears, as well as from the simultaneous activation of two stages.
Advantages and disadvantages of manual transmissions
All types of mechanisms have their own advantages and disadvantages. Consider them in manual transmission.
Merits:
- the design has the lowest cost when compared with peers;
- unlike hydromechanical, it has less weight and higher efficiency;
- does not need special cooling conditions compared to automatic transmissions;
- the average car with manual transmission has more economical parameters and acceleration dynamics, unlike the average car with automatic transmission;
- simplicity and engineering design;
- high degree of reliability and a large operational resource;
- does not need specific maintenance and scarce consumables or repair materials;
- the driver has a wider range of use of driving techniques in extreme conditions of icy, off-road, etc .;
- the car is easy to push and can be towed at any speed and at any distance;
- there is a technical possibility of complete separation of the engine and transmission in contrast to the hydromechanical automatic transmission.
disadvantages:
- to switch the transmission using a complete separation of the power plant and transmission, which affects the operation time;
- specific driving skills are required to ensure smooth shifting;
- the inability of the smooth switching gear ratio, since the number of stages is usually limited to a number from 4 to 7;
- low clutch unit life;
- the driver with long-term driving with a manual transmission there is more fatigue than when driving on an "automatic" transmission.
In most countries with higher incomes, the number of cars produced with manual transmission is reduced to almost 10-15%.



