Every driver at least once turned out to be literally a couple of seconds from the accident, when it is vital to have time to brake. However, to get up, as a car dug at the team can not. The distance that he will travel from the beginning of the braking to a full stop and is called the braking distance. To be able to estimate the stopping distance should be, so that it is always less than the distance to the disturbance on the way.
The length of the braking path depends on many different factors. Here and the driver's reaction, and the level of the braking system of the car, and external factors, such as the material of the track and weather conditions. And of course, the decisive role is played by the speed of the car at the time of braking. The question is - how to calculate the stopping distance of the car under all these conditions? For general calculations, three main factors are sufficient - the braking coefficient (Ke), the driving speed (V) and the coefficient of adhesion (FS) with the track.

Formula for calculating the braking distance of the car
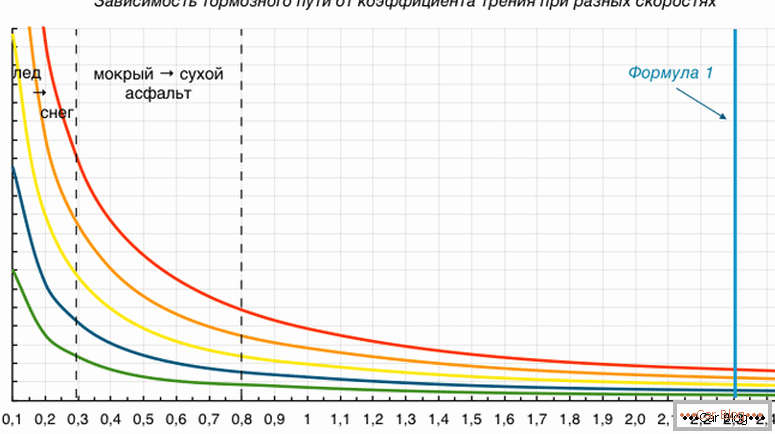
The formula from the table, which calculates the stopping distance, looks like this: S = Ke * V * V / (254 * FS). The brake coefficient of a regular light car is one. The coefficient of adhesion on a dry surface will be equal to 0.7. For example, take the case when the car moves on a dry road at a speed of 60 km / h. Then the stopping distance will be equal to 1 * 60 * 60 / (254 * 0.7) = 20.25 meters. On the ice (FS = 0.1), braking will last seven times longer - 141.7 meters!
By the result, we can see how much the stopping distance of the car from the table depends on the condition of the track and weather conditions.
Content
- 1 Braking in different conditions
- 2 Types of braking
- 3 Braking with ABS
- 4 How to determine the speed of the car on the braking distance?
Braking in different conditions
The stopping distance is inversely proportional to the coefficient of adhesion to the track. Simply put - the worse the road “holds”, the longer the car slows down. Let's look at the change in the coefficient (FS) in more detail:
- with dry asphalt - 0.7;
- on wet asphalt - 0.4;
- if the snow is rolled up - 0,2;
- icy road - 0.1.
These numbers allow us to see how the stopping distance will change depending on the conditions. As already mentioned, at a speed of 60 km / h on a dry road, the car will brake 20.25 meters, and on ice - 141.7. On a wet track, the braking distance will be 35.4 meters, and on a snowy road - 70.8.
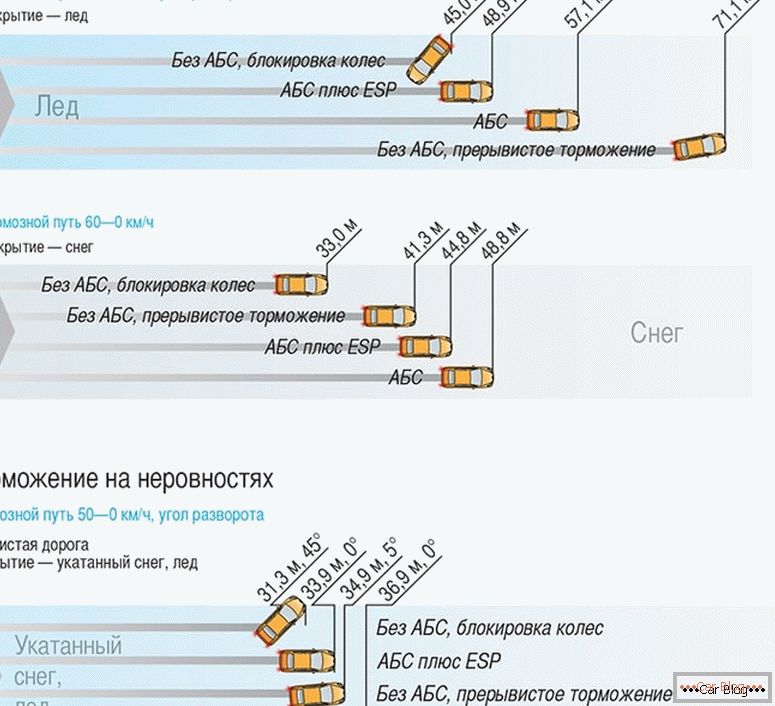
Types of braking
Types of braking
It should also be borne in mind that the braking method plays a big role:
- Sharp pressing can send the car into an uncontrollable skid.
- Gradually pressing the pedal will work with good visibility and time, but it does not apply in an emergency.
- Intermittent braking with a few presses of the pedal to the stop allows you to quickly stop the car, but also fraught with loss of control.
- Step press allows you to lock the wheels without losing contact with the pedal.
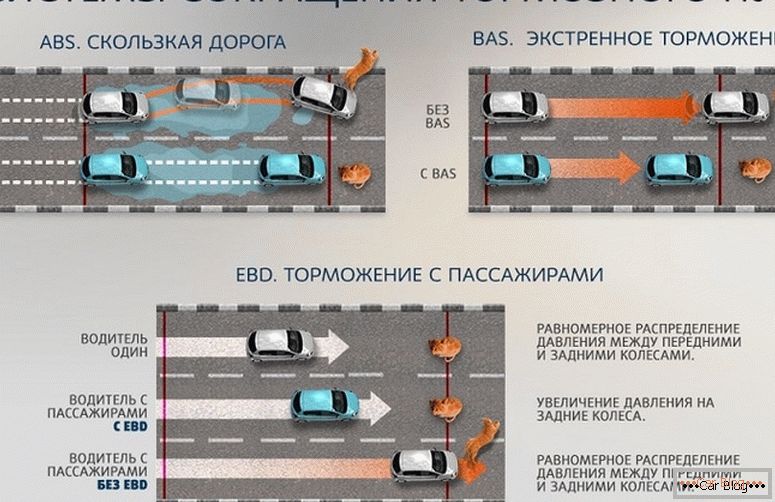
ABS braking
The ABS system works just by the principle of staged braking, and its main task is not to let the car go into an uncontrollable skid. ABS does not completely block the wheels, thereby leaving the driver control over the movement of the car. Extensive checks have shown that ABS will shorten the braking distance on dry or wet asphalt, and also works fine on gravel. But in other conditions, the system partially loses its value.
In winter conditions, ABS will increase braking distance by 15–30 meters when driving on snow or ice. In this case, the system will leave the driver control over the car, which may be critically important when driving on ice.
Friction table at different speeds
Remember, the weak spots of ABS are muddy earth and clay. On them, the braking distance can also be longer than with fully “manual” braking. But control over the car will also remain.
How to determine the speed of the car on the braking distance?
In those cases where it was still not possible to brake in time, it is necessary to determine how fast the vehicle was moving at the time of the start of braking. The general formula for calculating the “starting” deceleration rate looks like this - V = 0,5*t3*j + √2*S*j. In this case, the role played by the following factors:
- tZ - the rise time of the deceleration machine. Measured in seconds;
- j - slowing down the car when braking. Измеряется в м/c2. По ГОСТу на сухой трассе j=6,8 м;
- c2, and on wet - 5 m / s2;
- S - brake track length.
Возьмём условия, в которых tZ=0,3 секунды, тормозной след 20 метров, а трасса сухая. Тогда скорость равна 0,5*0,3*6,8 + √2*20*6,8 = 1,02 + 19,22 = 20,24 м/с = 72,86 км/ч.
Basically, three methods are used to determine the speed at the beginning of braking:
- Determination by stopping distance.
- Definition by the law of conservation of momentum.
- Determination of the deformation of the car.
ABS, EBD и BAS
The advantages of the first method are simplicity and speed, a large amount of research, an exact result. The second method is good because it can be used in the absence of traces of inhibition, it gives an accurate result and is useful in a collision with fixed machines. The third is different in that it takes into account the energy consumption for the deformation of the machine.
The disadvantages of each method are also different. In the first case, it is impossible to use in the absence of tire tracks. In the second - cumbersome calculations, and in the third - large volumes of what needs to be taken into account, and low accuracy of calculations.