>
The global auto industry is doing everything possible and impossible to meet the demands of more and more people. Every month dozens of new models are offered - if only there were plenty to choose from. Indeed, a long time ago, the times have sunk into oblivion, when on our roads one could find no more than a dozen different cars. And yet, any car owner, even on a subconscious level, seeks to make his personal car, if not exclusive, then easily recognizable among many of the same cars. This can be done in different ways, and installing new rims is one of them. Let for the uninformed such individualization seems very, very insignificant, in fact the replacement of the rim is able to radically change the appearance of the car. Note that this is not the only time when such an operation may be required. For example, an unsuccessful hitting a curb may cause defects that will be impossible or unprofitable to correct. In such cases, buying a new set is the only solution to the problem.

Features of the choice of disks for the car.
Как бы то ни было, но к вопросу выбора новых дисков для своего авто следует отнестись более чем ответственно, поскольку от этого зависит не только внешность машины, но и её ходовые качества. И даже если придерживаться рекомендаций производителя, это вовсе не гарантирует, что какой-либо из параметров покупки не окажется неподходящим. Конечно, можно воспользоваться услугами многочисленных онлайн-сервисов по подбору дисков по марке автомобиля, но далеко не все автовладельцы знают об их существовании, или вообще используют интернет для покупки запчастей, ориентируясь на советы знакомых «бывалых». А если учесть, что маркировка этих элементов ходовой части автомобиля может ввести в ступор любого, вопрос о том, как выбрать диски для авто, становится более чем актуальным.Читать далее про то как правильно выбрать диски для автомобиля-->
Kinds of rims
It is necessary to begin consideration of features of their design with such most common parameter as type of production. In accordance with the accepted classification, there are three main types of these products:
- stamped;
- cast;
- forged.
This, by the way, is also a matter of choosing the material for manufacturing discs - this is why you first need to decide on this characteristic, and only then begin to study other criteria that affect the driving characteristics of the car.
Stamped discs
By virtue of their low cost, such products are the most demanded (14-inch disks, installed regularly on most inexpensive cars, cost around 1 - 1.5 thousand rubles for one copy). They are made of “black” carbon rolled steel by means of separate punching of the front part and the rim, which are interconnected by welding. To protect against corrosion and environmental exposure, they are painted with enamel. Decorative plastic caps, which can be found in any auto shop, are intended for “stamping”. In addition to low prices, they have another significant advantage - high maintainability, which leads to their increased resource. The fact is that with any short-term mechanical action (hitting a speed in a deep hole, a collision with a concrete curb or other obstacle) they do not break - only dents remain. And this defect due to the high ductility of steel can be easily repaired by restoring the original disk geometry with high accuracy.
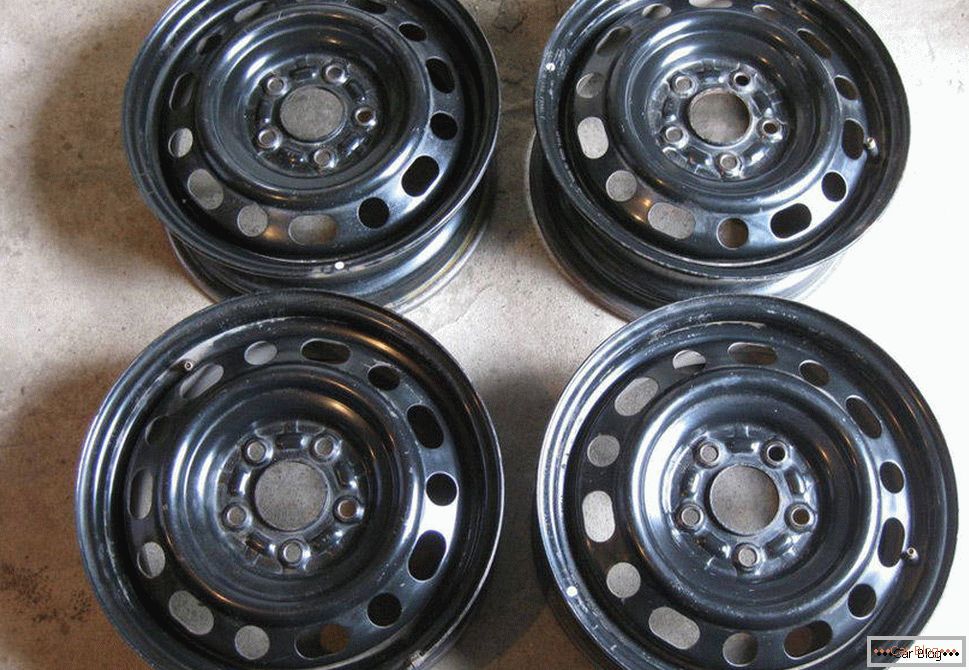

But there are stamped products and not less serious shortcomings. The main one is the heavy weight that weights the car, which entails both an increase in fuel consumption (albeit a slight one) and certain inconveniences during assembly / disassembly. The second significant drawback is the relatively low geometric accuracy of the “stamping”, which is why car owners often have problems with balancing the wheels, which are disrupted directly during the operation of the car. Finally, “stamping” is characterized by the least presentable appearance, and the above-mentioned decorative plates are designed to correct this deficiency.
Alloy wheels
By popularity, this kind of "shoe" for tires is in second place. They are often called light alloy because they are not made of steel - magnesium, aluminum or titanium alloy is used as the base material. The technology of their production is the casting of the product in the matrix. This allows, firstly, to significantly improve the accuracy of the disk geometry, and secondly, it allows you to easily change the design. After casting, the disks are subjected to additional processing - polishing and coating with paintwork material. The advantages of cast products are many:
- compared to stamped products, they weigh much less;
- alloy wheels more durable;
- made from materials that are not susceptible to corrosion, they last much longer;
- their higher thermal conductivity promotes better heat removal during braking;
- production technology allows for an arbitrarily high variety of design solutions.
In addition to using a matrix with different patterns, you can diversify a cast disk using painting in different colors. Why are they not as popular as stamped? The reason is quite banal - they also have a set of shortcomings, which in the eyes of most car owners outweigh their advantages.

Of course, the main limiting factor is the high price. The average cost of a 14-inch product is 3-4 thousand rubles. The second drawback is the low ductility of the material, which implies increased fragility of the products. Yes, the cast disk is able to withstand shocks of much greater force, but if it exceeds the strength threshold, the disk is likely to crack. Note that insufficient ductility is an increased load on other suspension assemblies due to the almost zero damping properties of alloy wheels. Another nuance that you should pay attention to when choosing rims: repair of alloy wheels is prohibited by the provisions of the regulations of the vehicle. And although the technology itself of repairing such products exists, it is truly unsafe to use it, since such a disc that has undergone recovery may cause an emergency situation.
Forged wheels
The main difference between forged products and cast products lies in the production technology - they are produced by the method of bulk stamping with subsequent additional processing. At the same time, the production material is the same aluminum alloys with the inclusion of titanium and magnesium. Stamping at high temperature is a process that allows you to preserve the internal structure of the material, while the exterior of the disc is finally determined during processing on a milling machine. Compared with cast prototypes, forged wheels are even easier, while increasing strength characteristics. Finally, the capabilities of modern milling machines are such that it is not a problem to give the product the required exclusive look with a given accuracy.
Do not forget that the plasticity of the forged disk, although inferior to "stamping", remains quite acceptable. Being subjected to a critically severe blow, such a disk is not likely to crack, but to get a dent, which to a certain extent makes it more maintainable. The main drawback of forging is the high cost: the manufacturing technology of such discs is the most complex and resource-intensive. Therefore, there are not too many manufacturers of such products, and you need to look for suitable forged wheels. The problem is aggravated by a large number of fakes made by casting, and it is quite difficult to distinguish a forged disk from a casting layman.

The parameters of the rims included in the marking
If you have decided on the type of disks for your car, it remains to consider in detail the characteristics that may be included in the labeling. It should be noted that there are many such parameters, and just remembering them can be problematic. If you choose stamping, it is enough to use specialized services, because their design is not very diverse and, in principle, is not important. But in the case of alloy wheels, their appearance becomes a priority criterion, and all the rest will have to be selected by yourself, so knowledge about them will be completely superfluous. We list the parameters that have a significant impact on how to choose the alloy wheels:
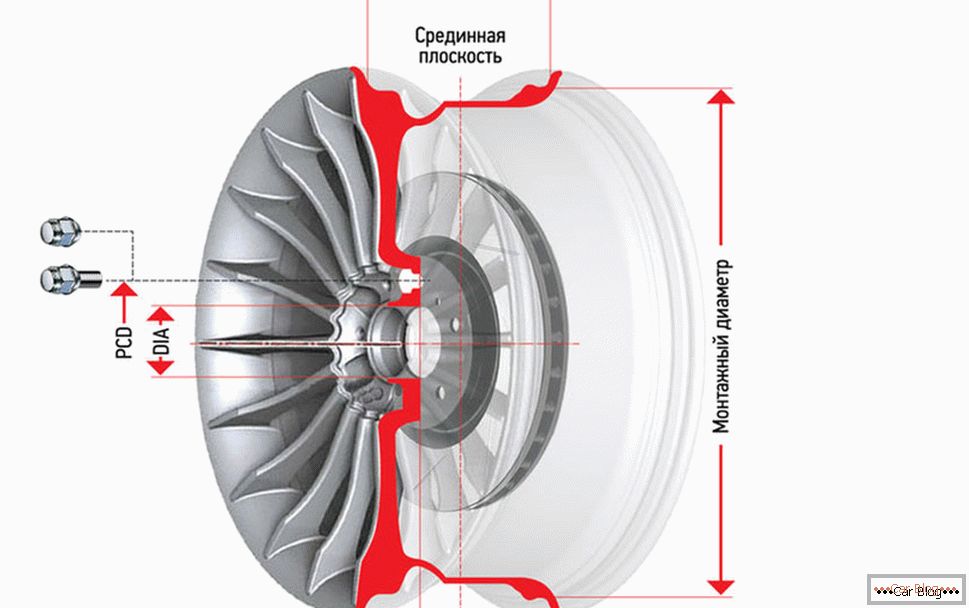
- mounting / mounting diameter;
- the number and size of the mounting holes (often abbreviated as PCD);
- disc reach (denoted by ET);
- disk width;
- the diameter of the hole under the wheel hub;
- the shape of the holes for mounting disks;
- presence / absence of the Humps.
Note that the order in which the selection criteria of a disc for a particular car model is listed is random, without prioritization.
Mounting size
This is perhaps the most well-known parameter, which is very easily interpreted, denoting the diameter of the outer circumference of an automobile disk, measured in inches. Usually it is denoted by the Latin letter R. If the label indicates, for example, R17, this means that the outer diameter of the disk is 17 inches. In fact, the diameter is denoted by the letter D, but in the automotive industry, it so happened that it was customary to indicate the diameter under the letter designating the radius, and this tradition first took root in the tire industry, and only then spread to the rims. But we use this parameter without even thinking about its physical meaning, knowing full well that it’s about the diameter. Most car owners know what the mounting size of the disks in their car. And beginners can easily find this feature in the user manual. Sometimes this size is indicated on a sticker located in the doorway (along with a recommendation for the allowable tire pressure). By the way, the mounting tire size is indicated by the same letter R and must match the mounting size of the disk. Well, the diameter of the tire of your car  Discounts for new cars! Profitable loan from 9.9% installments 0%
Discounts for new cars! Profitable loan from 9.9% installments 0%  adom.ru know almost everything.
adom.ru know almost everything.
Many tuning lovers choose wheels and tires larger than those specified by the manufacturer. But improving the appearance (by the way, quite controversial) is the only plus of such a decision. First, the increase in size may be incompatible with the existing geometry of the near-disk space, which may cause friction on the wheel arch liner during turns or shaking cars. Secondly, this decision is likely to change the functionality of the suspension, which usually becomes the cause of more rapid wear of the chassis. Finally, an increase in the diameter is associated with a decrease in the tire profile, which affects the decrease in driving comfort. However, changing the diameter set by the manufacturer by one inch in either direction is permissible, and without dangerous consequences for the vehicle.
Number / dimensions of mounting holes
This pair of parameters, called “razboltovka” in the professional environment, indicates the number of holes for mounting on the caliper, as well as the diameter of the circle on which these holes are located. In marking, this parameter is usually denoted by the abbreviation PCD (Pitch Circle Diameter, which, in fact, translates as "diameter of a circle"). The number of holes for mounting bolts can vary from three (usually on small cars) to eight or more. Let's say OKA PCD3x98, in most VAZ models - PCD 4 x 98, and Niva - PCD 5 x 139. The general rule is one thing: the greater the vehicle weight or the maximum speed with which it can move, the larger the circle diameter and the number of mounting holes.
Razboltovka - important parameter. For example, if you install Largus with a 4 x 100 PCD, 4 x 98 disks, nothing good will come out, despite the very small difference - just 2 millimeters. This is enough to properly tighten only one bolt, all the rest will be with a slight displacement, which will cause the wheel to beat during movement. And this is fraught with great trouble. This problem is partially solved by the use of bolts of a special design (with the so-called “floating cone”). However, it is not recommended to get involved in such experiments, and if you want to choose the disks for the car correctly, make sure that the PCD is completely identical to the one specified in the manual.
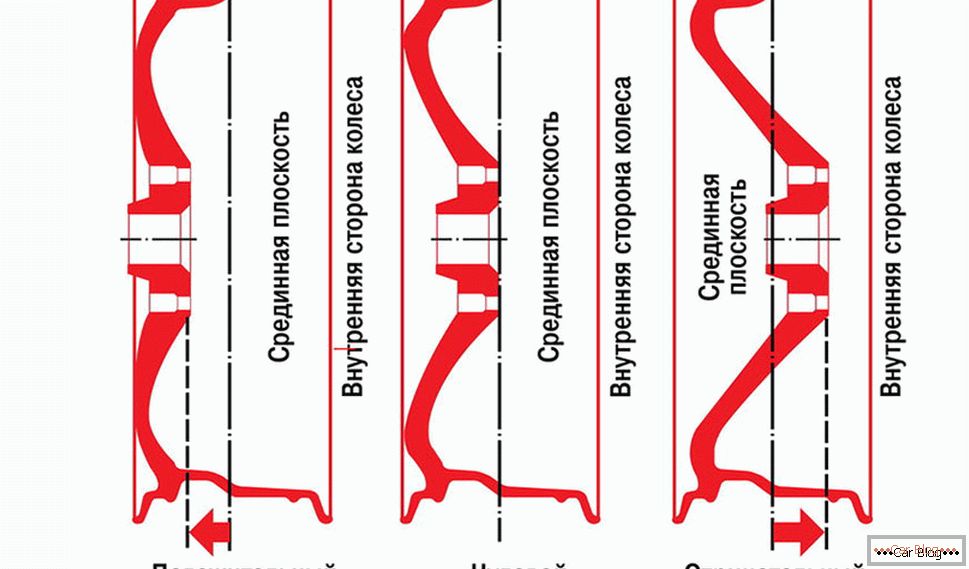
Disc crash
By this parameter, denoted by the abbreviation ET, we mean the distance between the longitudinal axis of symmetry and the mating plane. Visually, the longitudinal axis is the line that divides the disk into two equal parts in width. The restraining plane is the place where the disk contacts the hub. Its design may be different, with the departure takes both positive and neutral and negative values. It all depends on how its longitudinal axis of symmetry is located. If it is closer to the car than the attachment plane, they say a positive departure, if these conditional lines coincide, the disk has zero departure, and if the axis is closer to the wheel, the departure is negative. In other words, the larger the disk juts out - the smaller the departure, the deeper it goes into the wheel arch - the greater this value. When selecting discs for cars, you should also select products with departure parameters that are most similar to the recommended values. Otherwise, in addition to changing the characteristics of the track, you will get an increased effect on the hub bearings and the suspension as a whole, which accelerates the wear of the bearings and the undercarriage.
Disk width
As the diameter, the width of the disk is treated simply and unequivocally. In the adopted marking, it is usually denoted by the letter J and the number following it, indicating the width of the product in inches. In general, it is recommended not to violate this parameter, since it also affects the car’s handling (with a width slightly smaller than the standard), or leads to an increase in the load on the vehicle’s chassis in case of using too wide discs. In any case, this parameter is closely related to the tires, which are designed for car rims of a certain width.
Landing diameter
There should be no problems with the interpretation of this parameter. The diameter of the central hole, through which the disk is attached to the hub, is indicated on the label differently, depending on the regional standards - DIA or simply the letter D. It is clear that if you buy a disk with a smaller diameter than the standard diameter, you simply cannot install it. With the exact opposite error, its alignment will be disturbed if centering rings are not used. There is an erroneous opinion among motorists that if the bore diameter is larger than the standard one, it will be centered on its own, due to uniform tightening of the bolts. In practice, such an effect, if achieved, then acts briefly. In the end, there will still be a beating and vibration, especially when driving at high speeds, and if balancing does not solve the problem, it should be understood that the reason is the mismatch of the diameter of the central hole to the nominal size.
The shape of the mounting holes
This parameter is important from the point of view of matching the geometry of fasteners used to mount the disk to the hub. For conventional stamped products, the nuts and bolts have a barely noticeable bevel to fit snugly to the plane of the disk in the place of its connection with the hub. In addition, the bolts are quite short, due to the small thickness of this type of disks. The thickness of the cast product is noticeably larger, the mounting hole also has a slightly different shape. The geometry of the seat can be as conical, as well as take other forms. For example, flat or hemispherical. We have already mentioned the “floating cone” bolts, which are intended to partially compensate for the discrepancy between the PCD parameter and the standard size. In such a fastener, the conical working part is a separate ring placed directly on the bolt, which, when the bolt is tightened, moves along the longitudinal axis.
Hump
This incomprehensible word should be understood as special assembly protrusions that are present on the outwardly protruding surface. Their task is to fix a tubeless tire on a disk. Surely, you have often attended the tire mounting at tire service and heard the characteristic cotton, which is heard when the tire is inflated immediately after its installation. This sound occurs at the moment when the side ring of the tire completely sits between the edge of the disk and the Hump. As a result of a sharp drop in the tension of the rubber and there is a cotton, resembling a shot. It is necessary to recognize that today it is almost impossible to meet new disks focused on the use of tires requiring the installation of cameras. That is, they all have humps. Therefore, this parameter will be important only in the case when you met discs made unknown how long ago. The lack of a hampa is easy to see visually, it’s almost never paid attention to. Physically, it is also possible to install a modern tubeless tire on such products, but in this case it is impossible to guarantee complete tightness of the fitment by definition. And this, in turn, means that you expose your car along with everyone who is in it, a serious danger: if the tire pressure is insufficient, in sharp turns it can fly off the disk, which threatens to turn the car over.
As you can see, in some cases, buying discs that do not fully comply with the parameters of the recommended products is permissible, but always with reservations. If you are not inclined to take risks, discard the kit you like in favor of the one that is as similar in characteristics as those recommended by the automaker.



